Type 1, Type 2, CCS1, CCS2, GB/T Connectors: A Detailed Explanation, Differences, and AC/DC Charging Distinction
The use of different types of connectors is necessary to ensure safe and efficient energy transfer between electric vehicles and charging stations. Common EV Charger connector types include Type 1, Type 2, CCS1, CCS2 and GB/T. Each connector has its own characteristics to meet the requirements of different vehicle models and regions. Understanding the differences between these Connectors for EV Charging station is important in choosing the right EV charger. These Charging connectors differ not only in physical design and regional usage, but also in their ability to provide alternating current (AC) or direct current (DC), which will directly affect charging speed and efficiency. Therefore, when choosing a Car charger, you need to decide on the right type of connector based on your EV model and the charging network in your region.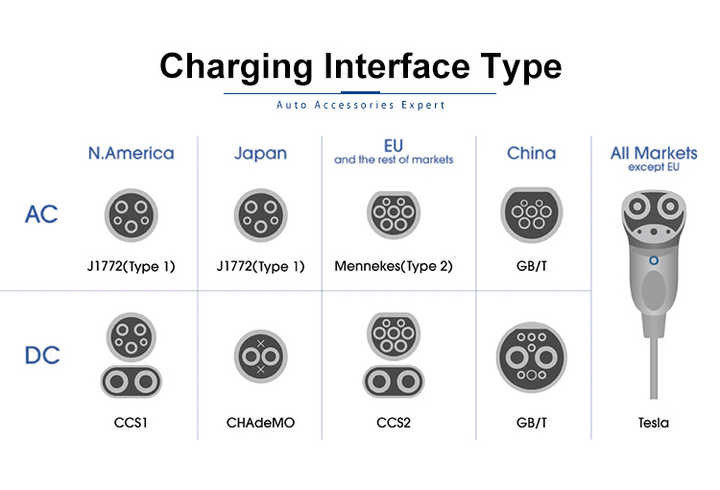
1. Type 1 Connector (AC Charging)
Definition: Type 1, also known as the SAE J1772 connector, is used for AC charging and is primarily found in North America and Japan.
Design: Type 1 is a 5-pin connector designed for single-phase AC charging, supporting up to 240V with a maximum current of 80A. It can only deliver AC power to the vehicle.
Charging Type: AC Charging: Type 1 provides AC power to the vehicle, which is converted into DC by the vehicle’s onboard charger. AC charging is generally slower compared to DC fast charging.
Usage: North America and Japan: Most American-made and Japanese electric vehicles, such as Chevrolet, Nissan Leaf, and older Tesla models, use Type 1 for AC charging.
Charging Speed: Relatively slow charging speeds, depending on the vehicle’s onboard charger and available power. Typically charges at Level 1 (120V) or Level 2 (240V).
2. Type 2 Connector (AC Charging)
Definition: Type 2 is the European standard for AC charging and is the most commonly used connector for EVs in Europe and increasingly in other parts of the world.
Design: The 7-pin Type 2 connector supports both single-phase (up to 230V) and three-phase (up to 400V) AC charging, which allows faster charging speeds compared to Type 1.
Charging Type: AC Charging: Type 2 connectors also deliver AC power, but unlike Type 1, Type 2 supports three-phase AC, which enables higher charging speeds. The power is still converted to DC by the vehicle’s onboard charger.
Usage: Europe: Most European automakers, including BMW, Audi, Volkswagen, and Renault, use Type 2 for AC charging.
Charging Speed: Faster than Type 1: Type 2 chargers can provide faster charging speeds, especially when utilizing three-phase AC, which offers more power than single-phase AC.

3. CCS1 (Combined Charging System 1) – AC & DC Charging
Definition: CCS1 is the North American standard for DC fast charging. It builds upon the Type 1 connector by adding two additional DC pins for high-power DC fast charging.
Design: The CCS1 connector combines the Type 1 connector (for AC charging) and two additional DC pins (for DC fast charging). It supports both AC (Level 1 and Level 2) and DC fast charging.
Charging Type: AC Charging: Uses Type 1 for AC charging.
DC Fast Charging: The two additional pins provide DC power directly to the vehicle’s battery, bypassing the onboard charger and delivering a much faster charging rate.
Usage: North America: Commonly used by American automakers such as Ford, Chevrolet, BMW, and Tesla (via an adapter for Tesla vehicles).
Charging Speed: Fast DC Charging: CCS1 can deliver up to 500A DC, allowing for charging speeds of up to 350 kW in some cases. This allows EVs to charge to 80% in about 30 minutes.
AC Charging Speed: AC charging with CCS1 (using the Type 1 portion) is similar in speed to the standard Type 1 connector.
4. CCS2 (Combined Charging System 2) – AC & DC Charging
Definition: CCS2 is the European standard for DC fast charging, based on the Type 2 connector. It adds two additional DC pins to enable high-speed DC fast charging.
Design: The CCS2 connector combines the Type 2 connector (for AC charging) with two additional DC pins for DC fast charging.
Charging Type: AC Charging: Like Type 2, CCS2 supports both single-phase and three-phase AC charging, allowing for faster charging compared to Type 1.
DC Fast Charging: The additional DC pins allow for direct DC power delivery to the vehicle’s battery, enabling much faster charging than AC charging.
Usage: Europe: Most European automakers like BMW, Volkswagen, Audi, and Porsche use CCS2 for DC fast charging.
Charging Speed: DC Fast Charging: CCS2 can deliver up to 500A DC, allowing vehicles to charge at speeds of 350 kW. In practice, most vehicles charge from 0% to 80% in around 30 minutes with a CCS2 DC charger.
AC Charging Speed: AC charging with CCS2 is similar to Type 2, offering single-phase or three-phase AC depending on the power source.

5. GB/T Connector (AC & DC Charging)
Definition: The GB/T connector is the Chinese standard for EV charging, used for both AC and DC fast charging in China.
Design: GB/T AC Connector: A 5-pin connector, similar in design to Type 1, used for AC charging.
GB/T DC Connector: A 7-pin connector, used for DC fast charging, similar in function to CCS1/CCS2 but with a different pin arrangement.
Charging Type: AC Charging: The GB/T AC connector is used for single-phase AC charging, similar to Type 1 but with differences in the pin design.
DC Fast Charging: The GB/T DC connector provides DC power directly to the vehicle’s battery for fast charging, bypassing the onboard charger.
Usage: China: The GB/T standard is used exclusively for EVs in China, such as those from BYD, NIO, and Geely.
Charging Speed: DC Fast Charging: GB/T can support up to 250A DC, providing fast charging speeds (although generally not as fast as CCS2, which can go up to 500A).
AC Charging Speed: Similar to Type 1, it offers single-phase AC charging at slower speeds compared to Type 2.
Comparison Summary:
| Feature | Type 1 | Type 2 | CCS1 | CCS2 | GB/T |
| Primary Use Region | North America, Japan | Europe | North America | Europe, Rest of World | China |
| Connector Type | AC Charging (5 pins) | AC Charging (7 pins) | AC & DC Fast Charging (7 pins) | AC & DC Fast Charging (7 pins) | AC & DC Fast Charging (5-7 pins) |
| Charging Speed | Medium (AC only) | High (AC + Three-phase) | High (AC + DC Fast) | Very High (AC + DC Fast) | High (AC + DC Fast) |
| Maximum Power | 80A (single-phase AC) | Up to 63A (three-phase AC) | 500A (DC fast) | 500A (DC fast) | 250A (DC fast) |
| Common EV Manufacturers | Nissan, Chevrolet, Tesla (Older Models) | BMW, Audi, Renault, Mercedes | Ford, BMW, Chevrolet | VW, BMW, Audi, Mercedes-Benz | BYD, NIO, Geely |
AC vs. DC Charging: Key Differences
| Feature | AC Charging | DC Fast Charging |
| Power Source | Alternating Current (AC) | Direct Current (DC) |
| Charging Process | Vehicle’s onboard charger converts AC to DC | DC is supplied directly to the battery, bypassing the onboard charger |
| Charging Speed | Slower, depending on power (up to 22kW for Type 2) | Much faster (up to 350 kW for CCS2) |
| Typical Usage | Home and workplace charging, slower but more convenient | Public fast charging stations, for quick turnaround |
| Examples | Type 1, Type 2 | CCS1, CCS2, GB/T DC connectors |
Conclusion:
Choosing the right charging connector largely depends on the region you are in and the type of electric vehicle you own. Type 2 and CCS2 are the most advanced and widely adopted standards in Europe, while CCS1 is predominant in North America. GB/T is specific to China and offers its own set of advantages for the domestic market. As EV infrastructure continues to expand globally, understanding these connectors will help you select the right charger for your needs.
Contact us to learn more about new energy vehicle charger Station
Post time: Dec-25-2024




